At least two British children have died from a Kawasaki-like disease linked to Covid-19, doctors have revealed.
In the largest study of its kind yet, paediatricians detailed the course of the mystery inflammatory illness in 78 hospitalised youngsters.
All were in intensive care and almost half were mechanically ventilated. Two children have already died and one is still in critical care.
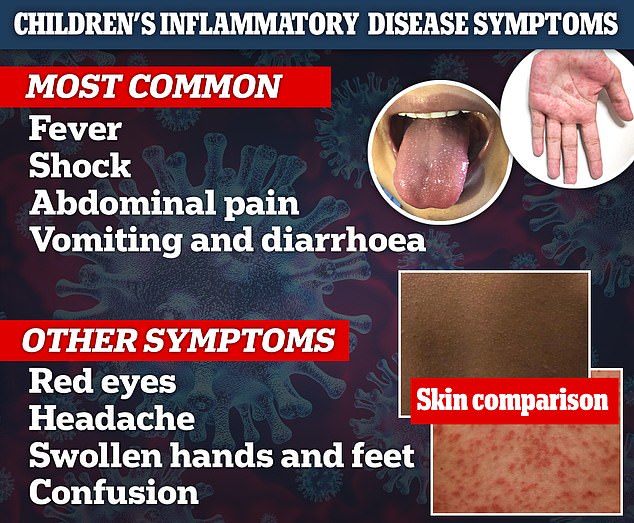
All the youngsters, who had an average age of 11, presented with a fever. Some had suffered shock, stomach pain, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Doctors from around the world have also reported ill children having a rash, red eyes and swollen feet.
Fatal complications of the illness appear to be related to strain on the heart – but the exact details of how the complication kills remain unclear.
Almost 80 per cent were from black, Asian and minority ethnic backgrounds (BAME). Scientists are currently baffled as to why this is.
Most children did not positive for Covid-19 with a swab test but did have antibodies, showing they had been infected in the past.
In the largest study of its kind yet, paediatricians detailed the course of the mystery inflammatory illness in 78 hospitalised youngsters. The most common symptoms were fever, shock, abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhoea. Other reported symptoms by other doctors are red eyes, a headache, swollen hands and feet and confusion
The illness has been likened to Kawasaki disease, which mainly affects under-fives and causes blood vessels throughout the body to swell.
It has been dubbed Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally (PIMS-TS) and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
There have been fewer than 200 cases of PIMS-TS reported in England so far, with a range of symptoms and severity. Most children have already recovered.
Nearly 300 cases the life-threatening syndrome have been identified in the US, in two studies published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Doctors are almost certain the illness is being caused by the coronavirus but they haven’t yet been able to prove it yet.
Children appear to fall sick with PIMS-TS several weeks after being infected by the coronavirus, called SARS-CoV-2.
The study, published in The Lancet, said hospital admissions to paediatric intensive care between April 1 and May 10 was at least 11-fold higher than historical trends for similar inflammatory conditions.
Dr Patrick Davies, consultant paediatric intensive care specialist at Nottingham Children’s Hospital, published the findings of 78 children across 21 of 23 UK paediatric intensive care units during that time period.
They each fulfilled the condition definition newly outlined by the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health to help both doctors and parents spot the signs.
A fever was present in all cases studied, and children also suffered with shock, abdominal pain, diarrhoea and vomiting.
They received a varied range of treatments, and one child was given the antiviral remdesivir – which became the first medication to get approval for use on the NHS to treat Covid-19 in May.
A third of patients were found to have coronary artery abnormalities. These included coronary aneurysms – the abnormal dilation of a artery supplying the heart.
Four per cent of patients had significant blood clotting that was affecting the blood flow in vessels.
Doctors believe the survival rate is high because three per cent (two) of children in the study died.
Dr Padmanabhan Ramnarayan, senior author of the research, told MailOnline: ‘While it is difficult to comment about the cause of death in individual cases, potential mechanisms for a poor outcome might include blood clots in the brain, excessive bleeding and severe heart failure.
‘However, this study shows that the condition is rare and has affected few children overall, and that outcomes for those who have needed ICU care is generally very good.’
He added that PIMS-TS is an inflammatory condition and causes a similar phenomenon to the ‘cytokine storm’ described in adults with Covid-19.
A cytokine stormy, potentially fatal, is when the immune response goes into overdrive and immune cells start attacking healthy tissue as well.
Dr Ramnarayan, a consultant in paediatric intensive care retrieval at Great Ormond Street Hospital, said: ‘[It] may lead to multiple organs being affected, mainly the heart, kidneys and blood vessels.’
Academics did not reveal who the children who died in the study cohort were. It is not clear they are two previously reported UK fatalities linked to Kawasaki and Covid – a 14-year-old boy and an eight month old baby.
The death of the unnamed 14-year-old boy, treated at Evelina London Children’s Hospital in May, was reported on May 13. He had been part of a cluster of cases of PIMTS at the hospital.
The baby, Alexander Parsons, who had no underlying health conditions, passed away after being admitted to Plymouth’s Derriford Hospital on April 6.
He had been diagnosed with Kawasaki disease the day of his death and suffered a ruptured aneurysm, but it is not clear if his case was linked with Covid-19, his parents said.
Dr Ramnarayan said clinicians across the world have already made tremendous progress in understanding PIMS-TS, The Sun reports.
‘However, many aspects of the condition remain unclear, such as why it only affects some children or what the long-term implications of having this condition are,’ he added.
Dr Barney Scholefield, senior author, said a wealth of information to help treat cases has been uncovered so far.
‘A large group of children’s intensive care clinicians from across the NHS have rapidly worked together to help understand this condition,’ the paediatric intensive care consultant at Birmingham Women’s and Children’s NHS Foundation Trust and researcher at the University of Birmingham said.
Lead researcher on the paper and consultant paediatric intensive care specialist at Nottingham Children’s Hospital, Dr Patrick Davies said the key to successful treatment is ‘close collaboration with many specialists’.
A study led by Imperial College London and published in the Journal of the American Medical Association last month revealed the key characteristics of the new condition.
PIMS-TS affects children aged nine on average, which is older than children with Kawasaki, typically four years old.
It presents more often with abdominal pains and diarrhoea alongside the common features such as persistent fever.
Blood tests showed patients with PIMS-TS had markers of inflammation and cardiac enzymes, which suggest the heart is under strain.
Kawasaki disease is known to damage the coronary artery in such a way that as the child grows the artery does not, leading to a reduction in the amount of blood that can reach the heart.
The researchers said they could not be certain the new illness is caused by Covid-19, but said 45 of the 58 children involved in their study, from eight England hospitals, had evidence of current or past coronavirus infection.
They said although PISMT is extremely rare, it can make a child ‘very ill’, and cause complications when left untreated.
Dr Julia Kenny, consultant in paediatric infectious diseases and immunology at Evelina London, said: ‘Our analysis has shown that this is indeed a new condition.
‘Untreated, there is a risk of severe complications in very unwell children, but with early identification and treatment the outcome is excellent, with the children we are reviewing after discharge completely well.’
Lead author Dr Elizabeth Whittaker, from the Department of Infectious Disease at Imperial College London, said: ‘For any parents worried about their children, I would urge them to follow their usual instincts – whatever would normally prompt you to visit your GP or A&E with your child still applies here.’
Four of five cases need intensive care and mechanical ventilation, a study by Boston Children’s Hospital suggests, which was also supported by a study in New York.
Of the combined 281 cases studied, and reported in The New England Journal of Medicine in June, six patients died.
Top medics fear children could be at risk of suffering deadly heart damage if Kawasaki disease is misdiagnosed as coronavirus.
A British Kawasaki charity warned if actual cases of Kawasaki disease were misdiagnosed as Covid-19, it could leave children at risk of permanent heart damage.